
The temperature has been achieved (over 100 million degrees), however confining the hot fuel plasma using powerful magnetic fields has taken a while to perfect. Why Fission and fusion are two processes that alter the nucleus of an atom. Vocabulary Fission, fusion, transmutations, and nuclide. Understand the conservation laws that apply to nuclear reactions. There is no chain reaction involved – hence there can not be an explosion – the reaction is achieved simply by getting the fuel hot enough and containing it tightly enough for the components to collide and fuse. Name: Nuclear Fission and Fusion Date: Learning Objectives Compare and contrast nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. This chain reaction is the key to fission reactions, but it can lead to a runaway process, as in a nuclear bomb.įusion is a much harder reaction to achieve, however it yields more energy than fission. The result of the instability is the nucleus breaking up (in any one of many different ways), in the process producing more neutrons, which in turn hit more uranium atoms and make them unstable and so on. Both reactions release energy which, in a power plant, would be used to boil water to drive a steam generator, thus producing electricity.įission is triggered by uranium absorbing a neutron, which renders the nucleus unstable.
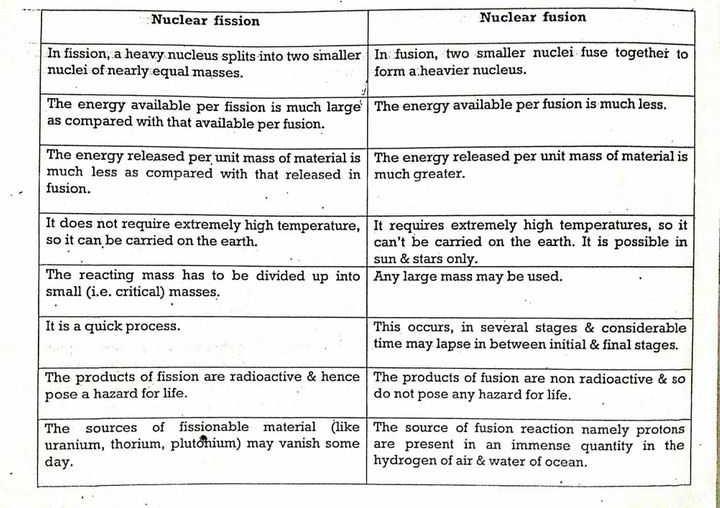
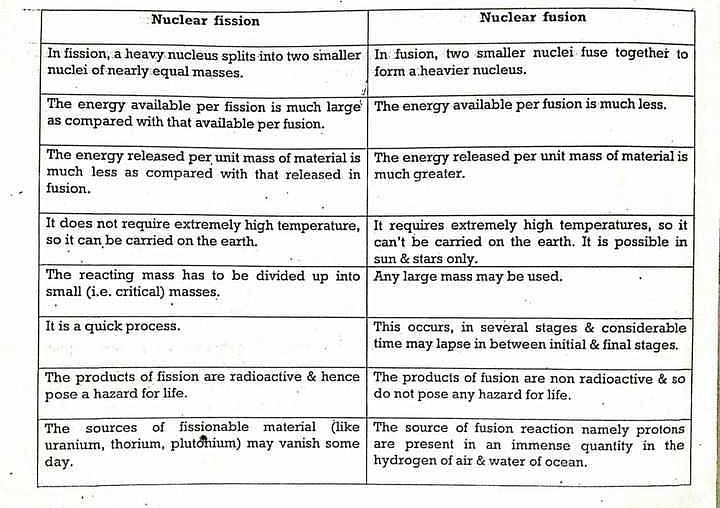
In fission, energy is gained by splitting apart heavy atoms (uranium) into smaller atoms (such as iodine, caesium, strontium, xenon and barium, to name just a few) whereas fusion is combining light atoms (in current experiments two isotopes of hydrogen, deuterium and tritium), which form a heavier one (helium).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
